Manage Domains Using Smart Contracts
This guide covers how to manage UD domain records using proxy contracts. This process requires using the Etherscan, Polygonscan, and Basescan user interface to write and execute contracts.
Step 1: Select a UNS Registry Smart Contract
The UNS Registry smart contract is where domain owners store their data and is a map of domain namehashes to key-value dictionaries of records. Choose one of the Unstoppable Registry smart contracts to interact with below.
info
For help identifying which Registry to use for which TLD, refer to the meta object returned from the supported TLDs endpoint. Use the registry that aligns with the registrationBlockchain for your TLD.

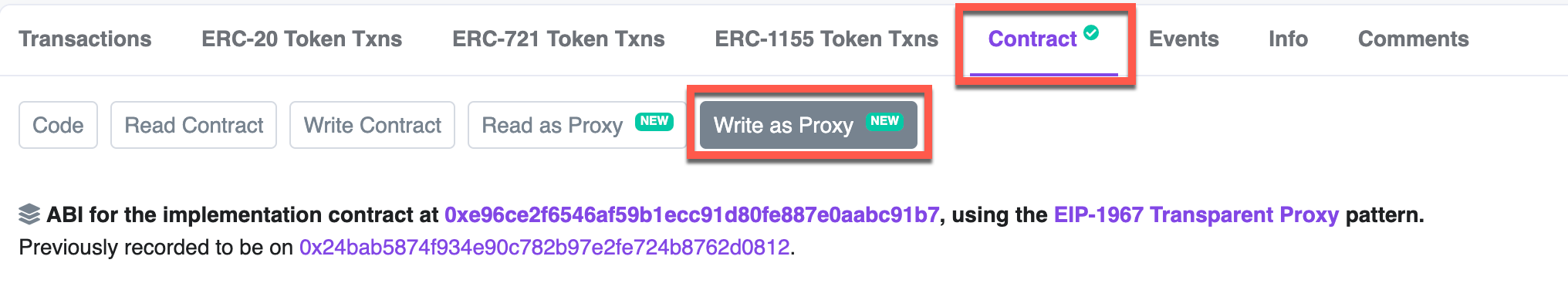
Step 2: Open the "Write as Proxy" Tab for the Registry Contract
Navigate to the Contract tab in either the Etherscan or Polygonscan page of the Registry contract and click on the Write as Proxy tab:
Step 3: Connect Your Web3 Wallet
Click on the Connect to Web3 button in the Write as Proxy tab and connect the wallet associated with the domain:


Step 4: Manage the Domain Records
Choose the set or setMany method from the Write as Proxy tab section. The set method allows you to update a single record, while the setMany method allows you to update multiple records simultaneously.
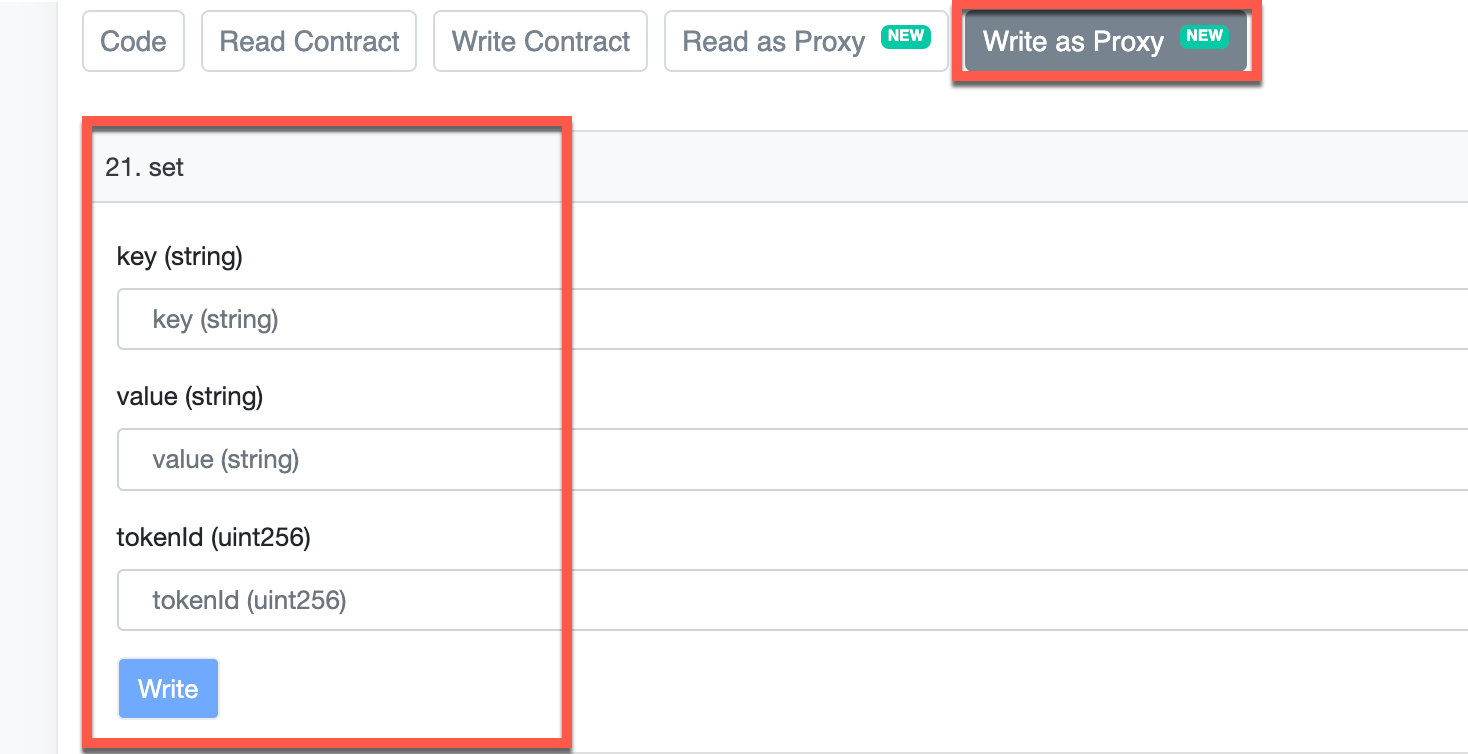
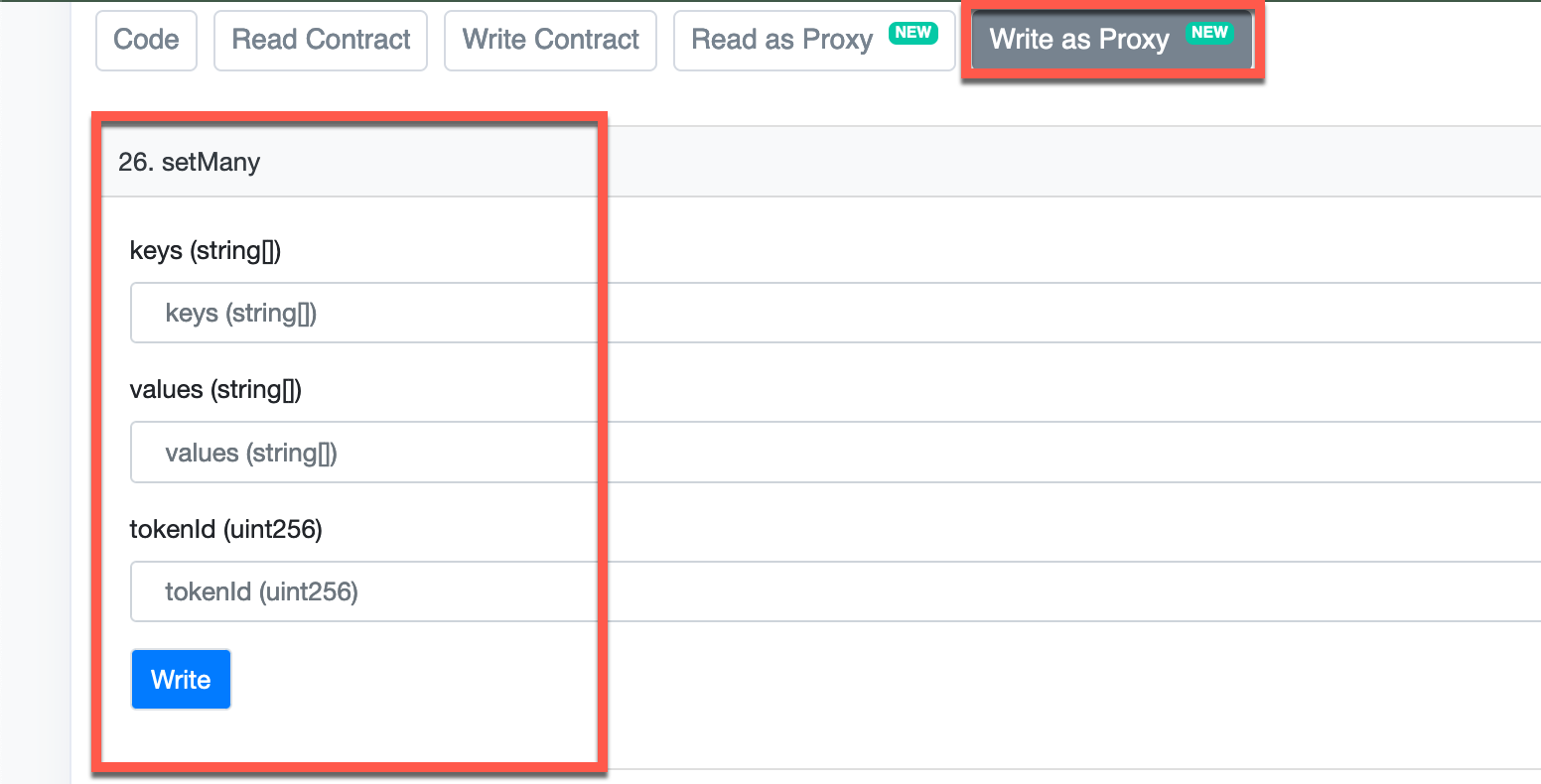
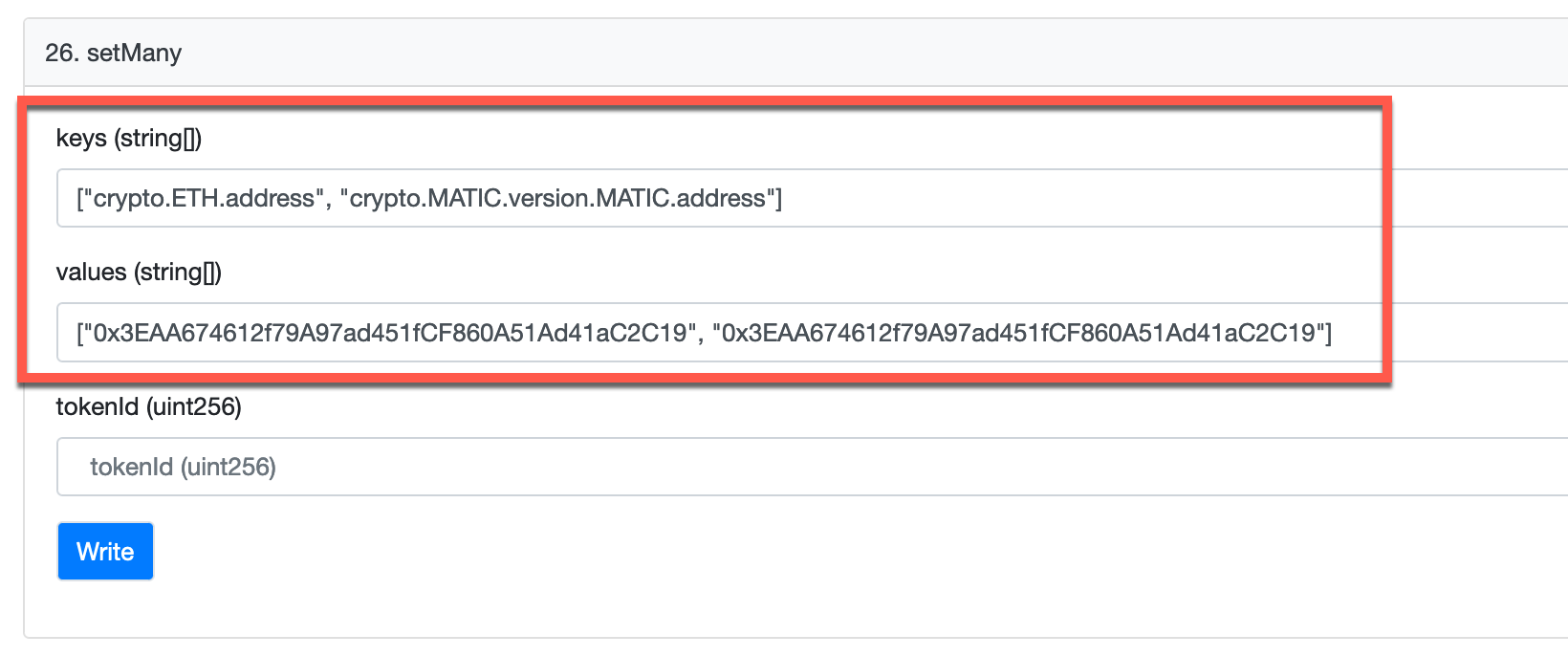
Next, add the record(s) you want to manage to the key and value fields as a single value for the set method or array of values for the setMany method.
info
Please see the Record Reference guide and reference JSON file for all the resolver keys used by the Unstoppable Domains UNS Registry.
Step 5: Generate the Namehash of the Domain
You can generate the namehash of a domain using the Resolution Service. You can also use online tools to calculate the namehash of the domain.
/**
* Resolves the namehash for a given domain.
*
* @param {string} domain - The domain name to resolve
* @returns {Promise<string | null>} The resolved namehash or null if not found
*
* @throws {Error} When no namehash can be resolved for the given domain
*/
async function resolveNamehash(
domain: string,
): Promise<string | null> {
try {
const response = await axios.get(
UNSTOPPABLE_API_BASE_URL + 'domains/' + encodeURIComponent(domain),
{
headers: { 'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + UNSTOPPABLE_API_KEY }
}
);
const metadata = response.data.meta;
const namehash = metadata['namehash'];
if (namehash) return namehash;
throw new Error('No namehash found for ' + domain);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Namehash resolution error:', error);
return null;
}
}After generating the domain namehash, insert it into the tokenId field of the set or setMany method.
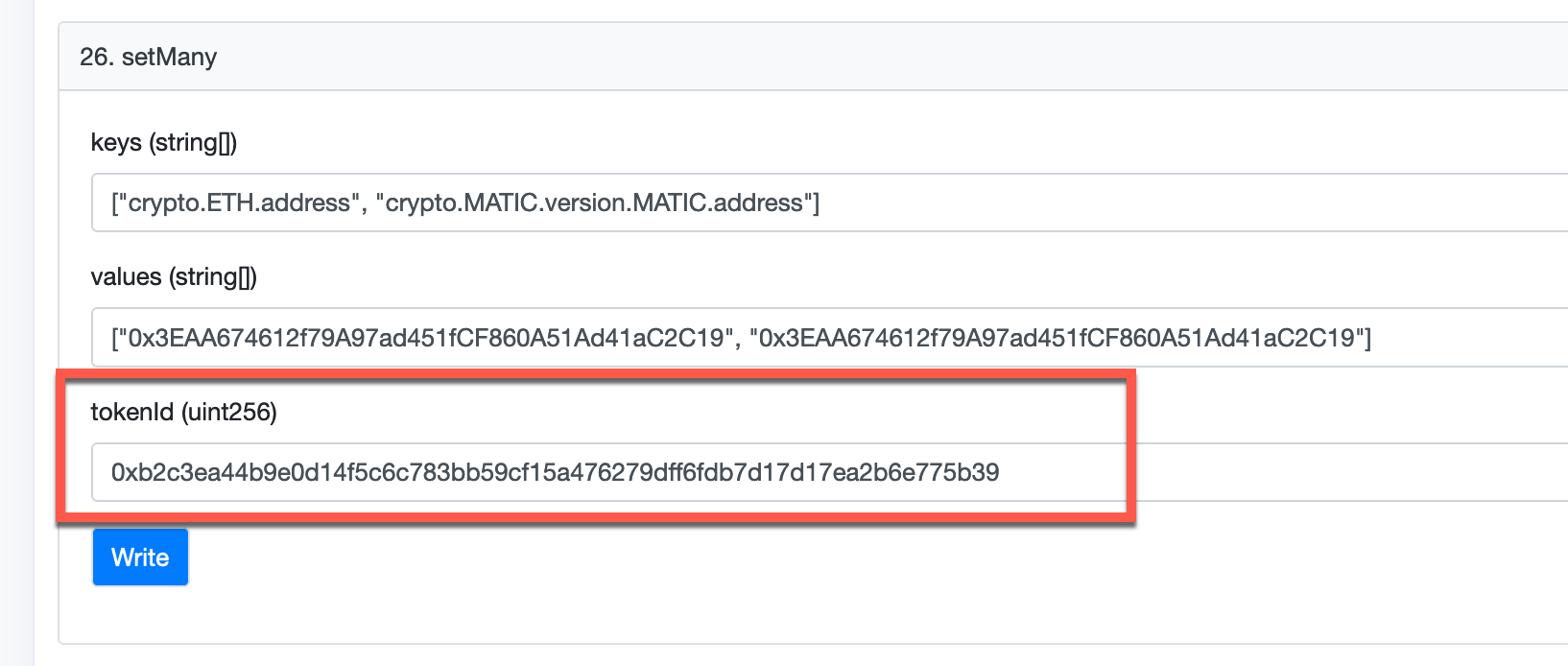
Step 6: Execute the Contract
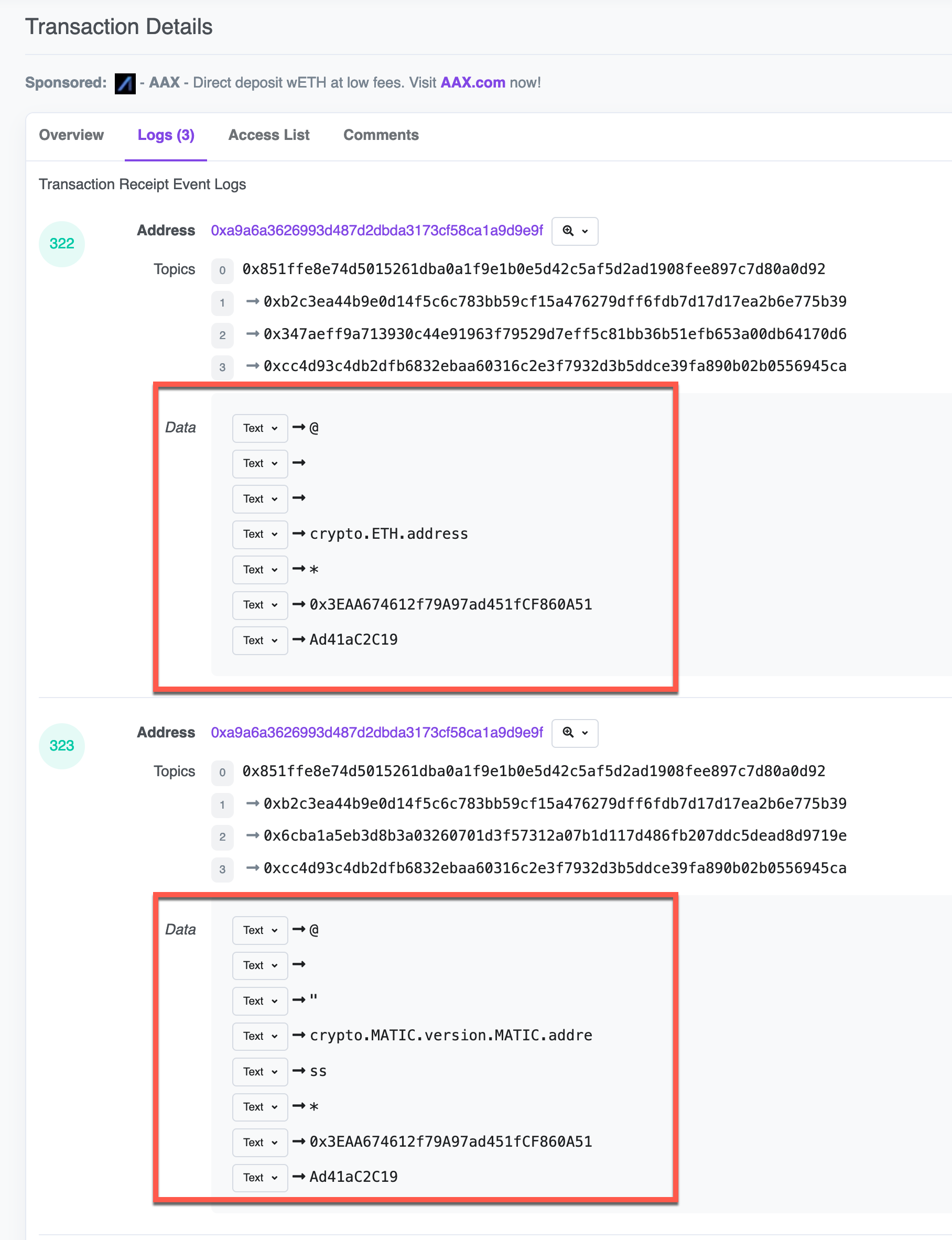
Click the Write button to sign the transaction and execute the contract. After signing the transaction, you can view its details on the blockchain explorer, like so:
Congratulations!
You have successfully managed your Unstoppable Domain records using smart contracts. Happy hacking!